0.0.1 ↑ 62. Hausaufgabe
0.0.1.1 ↑ Aufgabe 3 der Test-SA
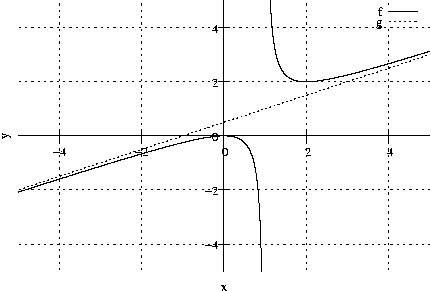
Gegeben: \mathrm{f}: x \mapsto \mathrm{f}(x) = \dfrac{x^2}{2x - 2}; \quad D_{\mathrm{f}} = \mathds{R} \setminus \left\{ 1 \right\};
- a)
Bestimme die Monotoniebereiche von \mathrm{f} und schließe damit auf die Art und Lage der Extrema von \mathrm{f}.
\mathrm{f}'(x) = \ldots = 2x \dfrac{x - 2}{\left(2x - 2\right)^2};
\mathrm{f} ist sms in \left]-\infty, 0\right[ und \left]2, \infty\right[;
\mathrm{f} ist smf in \left]0, 1\right[ und \left]1, 2\right[;
P_{\mathrm{HOP}}(0, 0); \quad P_{\mathrm{TIP}}(2, 2); \quad Uendlichkeitsstelle mit VZW bei x = 1;
- b)
Gegeben ist ferner die Funktion \mathrm{g}: x \mapsto \mathrm{g}(x) = \dfrac{x}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2}. Berechne \lim\limits_{x \to \infty}\left[\mathrm{f}(x) - \mathrm{g}(x)\right] und deute dieses Ergebnis geometrisch!
\lim\limits_{x\to\infty}\left[\dfrac{x^2}{2x - 2} - \dfrac{x + 1}{2}\right] = \lim\limits_{x\to\infty}\left[\dfrac{x^2 - \left(x + 1\right)\left(x - 1\right)}{2\left(x - 1\right)}\right] = \lim\limits_{x\to\infty}\left[\dfrac{x^2 - x^2 + 1}{2\left(x - 1\right)}\right]; ⇒ \mathrm{f}(x) - \mathrm{g}(x) \to 0 für x \to \infty;
\mathrm{g}(x) ist eine Asymptote von \mathrm{f}(x);