1 ↑ Mathematik: Infinitesimalrechnung
1.1 ↑ Schulheft
1.1.1 ↑ Funktion
Unter dem Begriff "Funktion" versteht man eine eindeutige Zuordnung einer Ausgangsmenge (Definitionsmenge \mathds{D}) auf eine Bildmenge (Wertemenge \mathds{W}):
x \in \mathds{D} \longmapsto y \in \mathds{W}
1.1.2 ↑ Typen von mathematischen Funktionen
- Polynomfunktionen:
Konstante Funktion: f\left(x\right) = c
Lineare Funktion: f\left(x\right) = mx + t
Quadratische Funktion: f\left(x\right) = ax^2 + bx + c
Kubische Funktion: f\left(x\right) = ax^3 + bx^2 + cx + d
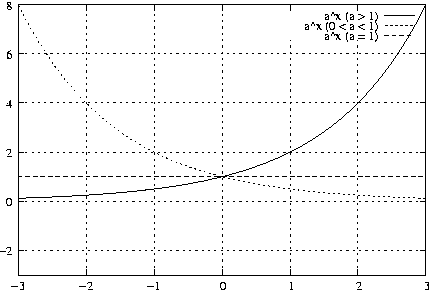
- Exponentialfunktion:
f\left(x\right) = a^x (a > 0)
- Logarithmusfunktion:
f\left(x\right) = \log_b x (b \in \mathds{R}^+ \setminus \left\{ 1 \right\})
- Wurzelfunktion:
f\left(x\right) = \sqrt{x} (\mathds{D} = \mathds{R}_0^+ = \mathds{W})
- Trigonometrische Funktionen:
\sin x, \mathds{D} = \mathds{R}
\cos x, \mathds{D} = \mathds{R}
\tan x, \mathds{D} = \mathds{R} \setminus \left\{ \frac{\pi}{2} + k\cdot{}\pi, k \in \mathds{Z} \right\}
- Gebrochenrationale Funktionen:
Z.B.: \frac{1}{x}, \frac{2x}{x^2-1}, \frac{3x^5-7x}{5x^3+2x+1}